Unlocking Anti-Aging Potential Through AMPK Activation and Cellular Rejuvenation*
Berberine, a bioactive compound extracted from several plants such as Coptis chinensis and Berberis vulgaris (barberry), has garnered attention for its anti-aging potential. One of the key mechanisms of Berberine is its activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), often referred to as a "metabolic master switch."* [1] Activation of AMPK improves metabolic efficiency and energy homeostasis, which are crucial for slowing down the aging process. Enhanced AMPK activity is associated with reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and promotes the removal of damaged cells through autophagy, thus preventing the accumulation of cellular debris and supporting cellular rejuvenation.

Combating Metabolic Disorders*
Additionally, Berberine has shown promise in managing metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity, which are closely linked with accelerated aging.* By improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver, Berberine helps manage blood sugar levels and lipid metabolism, potentially reducing the risk of metabolic issues.*
A unique quality of Berberine is its suspected ability to inhibit ROCK2, PIK3CD, KCNMA1, CSF1R, and KIT Kinase enzymes, and in a 2023 study, it was suggested that Berberine is similar to nature's own version of Dasatin1b, the powerful ingredient used in the groundbreaking D+Q senolytic treatment, a combination of Dasatin1b and Quercetin.* [2] Dasatinib is known to be a powerful CSF1R inhibitor. Berberine's association with CSF1R inhibition is why it was chosen for NEUROmergence.*

A Millennia-Old Remedy in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Berberine has been utilized in traditional medicine systems for centuries. Its use dates back over 2,000 years in ancient Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine, where it was valued for its broad spectrum of therapeutic benefits [3]. Historically, Berberine was employed to treat digestive disorders, including diarrhea and dysentery, due to its potent antimicrobial properties. It was also used for its anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects, helping to alleviate fever and reduce inflammation. In traditional Chinese medicine, Berberine was often included in formulas to balance the body's internal environment, improve gastrointestinal health, and support overall vitality. Its historical applications underscore its longstanding role as a versatile remedy, with modern research increasingly validating its efficacy and expanding its potential uses, particularly in managing metabolic disorders and supporting metabolic health.*
ATTENTION:
If pregnant, nursing, or trying to conceive, do not use this product. If you take medications, have preexisting conditions, or suffer from allergies of any kind, please consult your physician before taking this, or any other dietary supplements. The information contained on this site has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Please be aware that findings from animal studies and research on human cell lines may not necessarily reflect outcomes observed in humans. We encourage you to do your own research, and consult your physician before taking this or any other dietary supplements.
ABOUT MDS LABS

CITATIONS:
[1] Jin Y, Liu S, Ma Q, Xiao D, Chen L. Berberine enhances the AMPK activation and autophagy and mitigates high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 5;794:106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.11.037. Epub 2016 Nov 22. PMID: 27887947.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27887947/
[2] Singh NK, Dhanasekaran M, Kumar AHS. Pharmacology of Berberine and Its Metabolites, Is It the Natures Ozempic or Imatinib? Arch Pharmacol Ther. 2023;5(1):67-81.
https://www.scientificarchives.com/article/pharmacology-of-berberine-and-its-metabolites-is-it-the-natures-ozempic-or-imatinib
[3] Anil Kumar, Ekavali, Kanwaljit Chopra, Madhurima Mukherjee, Raghavender Pottabathini, Dinesh K. Dhull, Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update, European Journal of Pharmacology, Volume 761, 2015, Pages 288-297, ISSN 0014-2999, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.068.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299915300571
Unlocking Anti-Aging Potential Through AMPK Activation and Cellular Rejuvenation*
Berberine, a bioactive compound extracted from several plants such as Coptis chinensis and Berberis vulgaris (barberry), has garnered attention for its anti-aging potential. One of the key mechanisms of Berberine is its activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), often referred to as a “metabolic master switch.”* [1] Activation of AMPK improves metabolic efficiency and energy homeostasis, which are crucial for slowing down the aging process. Enhanced AMPK activity is associated with reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and promotes the removal of damaged cells through autophagy, thus preventing the accumulation of cellular debris and supporting cellular rejuvenation.

Combating Metabolic Disorders*
Additionally, Berberine has shown promise in managing metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity, which are closely linked with accelerated aging.* By improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver, Berberine helps manage blood sugar levels and lipid metabolism, potentially reducing the risk of metabolic issues.*
A unique quality of Berberine is its suspected ability to inhibit ROCK2, PIK3CD, KCNMA1, CSF1R, and KIT Kinase enzymes, and in a 2023 study, it was suggested that Berberine is similar to nature’s own version of Dasatin1b, the powerful ingredient used in the groundbreaking D+Q senolytic treatment, a combination of Dasatin1b and Quercetin.* [2] Dasatinib is known to be a powerful CSF1R inhibitor. Berberine’s association with CSF1R inhibition is why it was chosen for NEUROmergence.*

A Millennia-Old Remedy in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Berberine has been utilized in traditional medicine systems for centuries. Its use dates back over 2,000 years in ancient Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine, where it was valued for its broad spectrum of therapeutic benefits [3]. Historically, Berberine was employed to treat digestive disorders, including diarrhea and dysentery, due to its potent antimicrobial properties. It was also used for its anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects, helping to alleviate fever and reduce inflammation. In traditional Chinese medicine, Berberine was often included in formulas to balance the body’s internal environment, improve gastrointestinal health, and support overall vitality. Its historical applications underscore its longstanding role as a versatile remedy, with modern research increasingly validating its efficacy and expanding its potential uses, particularly in managing metabolic disorders and supporting metabolic health.*

ATTENTION:
If pregnant, nursing, or trying to conceive, do not use this product. If you take medications, have preexisting conditions, or suffer from allergies of any kind, please consult your physician before taking this, or any other dietary supplements. The information contained on this site has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Please be aware that findings from animal studies and research on human cell lines may not necessarily reflect outcomes observed in humans. We encourage you to do your own research, and consult your physician before taking this or any other dietary supplements.
ABOUT MDS LABS

CITATIONS:
[1] Jin Y, Liu S, Ma Q, Xiao D, Chen L. Berberine enhances the AMPK activation and autophagy and mitigates high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 5;794:106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.11.037. Epub 2016 Nov 22. PMID: 27887947.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27887947/
[2] Singh NK, Dhanasekaran M, Kumar AHS. Pharmacology of Berberine and Its Metabolites, Is It the Natures Ozempic or Imatinib? Arch Pharmacol Ther. 2023;5(1):67-81.
https://www.scientificarchives.com/article/pharmacology-of-berberine-and-its-metabolites-is-it-the-natures-ozempic-or-imatinib
[3] Anil Kumar, Ekavali, Kanwaljit Chopra, Madhurima Mukherjee, Raghavender Pottabathini, Dinesh K. Dhull, Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update, European Journal of Pharmacology, Volume 761, 2015, Pages 288-297, ISSN 0014-2999, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.068.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299915300571


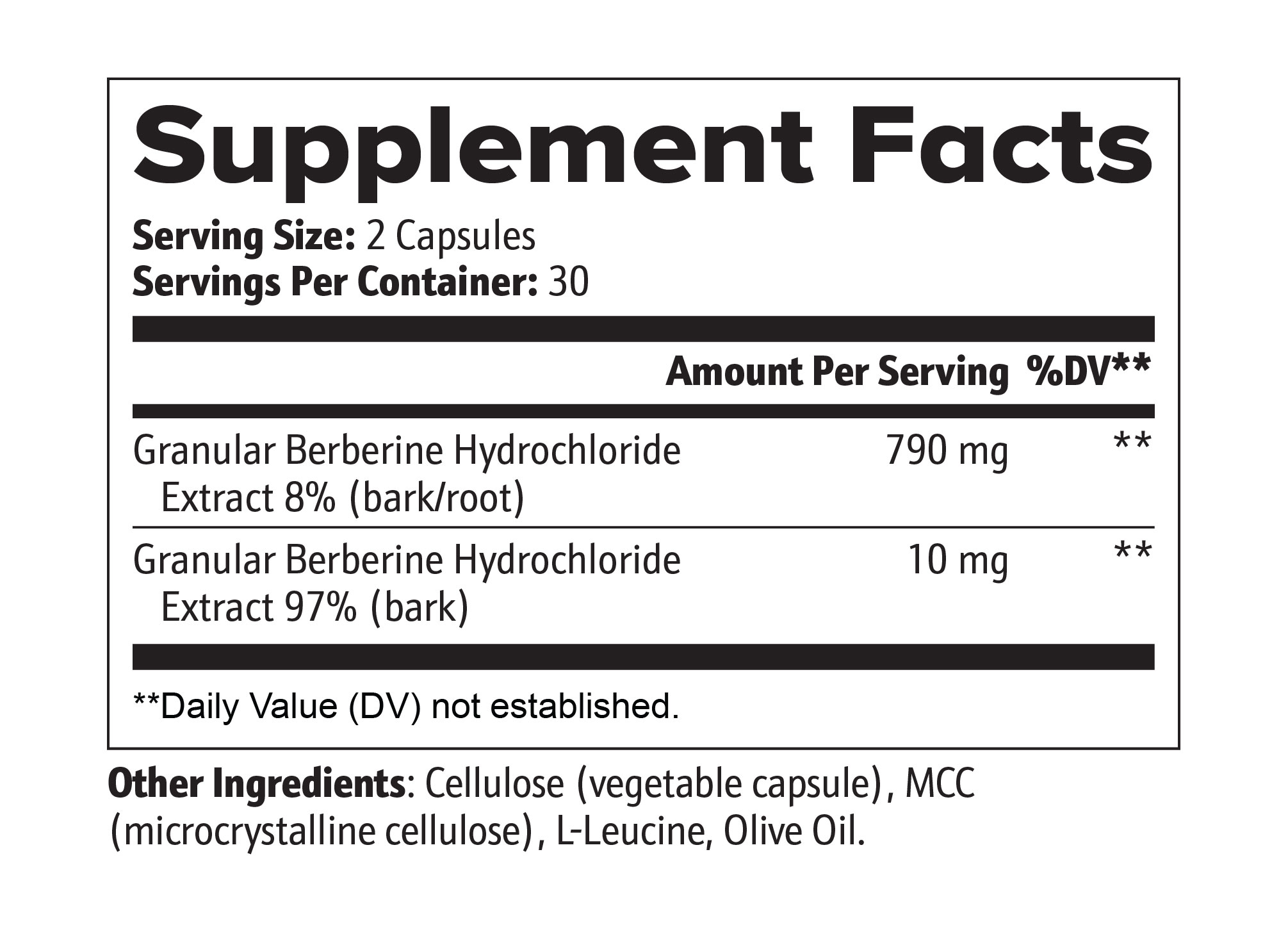
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.